We use cookies to offer you a better experience. For more information on how we use cookies you can read our Cookie and Privacy Policy.
A Guide to 3D Printing Materials
February 18, 2019
So which materials do 3D printers use to print anyhow? This is a common refrain from those unfamiliar with how 3D printers like the HP Metal Jet render physical objects, and even those more familiar with the 3D printing process may be surprised to find out there are other lesser known printing materials, from chemical elements to precious earth metals to commonplace Lego® bricks.
View our detailed infographic below to find out all there is to know about today's many 3D printing applications, their various source materials, and each material's environmental friendliness.
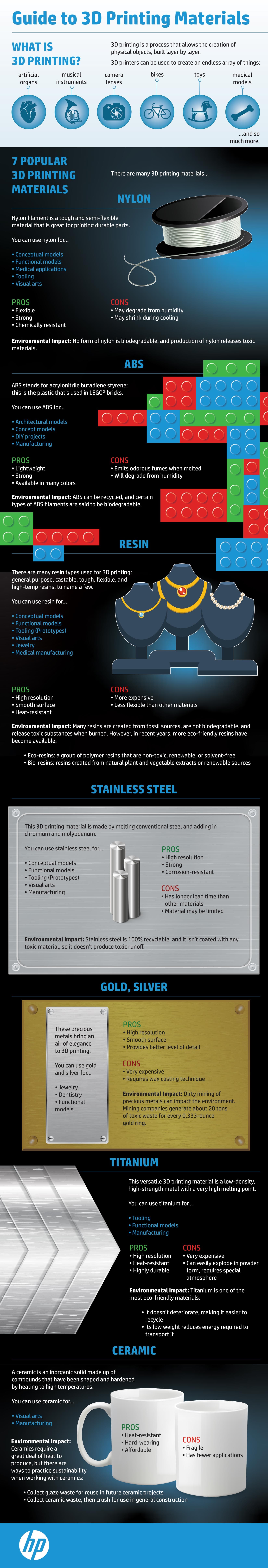
Infographic transcription:
What is 3D printing?
3D printing is a process that allows the creation of physical objects, built layer by layer.
3D printers can be used to create an endless array of things:
- Artificial organs
- Musical instruments
- Camera lenses
- Bikes
- Toys
- Medical models
- ...and so much more
7 popular 3D printing materials
There are many 3D printing materials available…
Nylon
Nylon filament is a tough and semi-flexible material that is great for printing durable parts.
You can use nylon for:
- Conceptual models
- Functional models
- Medical applications
- Tooling
- Visual arts
Pros:
- Flexible
- Strong
- Chemically resistant
Cons:
- May degrade from humidity
- May shrink during cooling
Environmental impact: No form of nylon is biodegradable, and production of nylon releases toxic materials.
ABS
ABS stands for acrylonitrile butadiene styrene; this is the plastic that’s used in Lego® bricks.
You can use ABS for:
- Architectural models
- Concept models
- DIY projects
- Manufacturing
Pros:
- Lightweight
- Strong
- Available in many colors
Cons:
- Emits odorous fumes when melted
- Will degrade from humidity
Environmental impact: ABS can be recycled, and certain types of ABS filaments are said to be biodegradable.
Resin
There are many resin types used for 3D printing: general purpose, castable, tough, flexible, and high-temp resins, to name a few.
You can use resin for:
- Conceptual models
- Functional models
- Tooling (Prototypes)
- Visual arts
- Jewelry
- Medical manufacturing
Pros:
- High resolution
- Smooth surface
- Heat-resistant
Cons:
- More expensive
- Less flexible than other materials
Environmental impact: Many resins are created from fossil sources, are not biodegradable, and release toxic substances when burned.
However, in recent years, more eco-friendly resins have become available.
- Eco-resins: a group of polymer resins that are non-toxic, renewable, or solvent-free
- Bio-resins: resins created from natural plant and vegetable extracts or renewable resources
Stainless steel
This 3D printing material is made by melting conventional steel and adding in chromium and molybdenum.
You can use stainless steel for:
- Conceptual models
- Functional models
- Tooling (Prototypes)
- Visual arts
- Manufacturing
Pros:
- High resolution
- Strong
- Corrosion-resistant
Cons:
- Has longer lead time than other materials
- Material may be limited
Environmental impact: Stainless steel is 100% recyclable, and it isn’t coated with any toxic material, so it doesn’t produce toxic runoff.
Gold, silver
These precious metals bring an air of elegance to 3D printing.
You can use gold and silver for:
- Jewelry
- Dentistry
- Functional models
Pros:
- High resolution
- Smooth surface
- Provides better level of detail
Cons:
- Very expensive
- Requires wax casting technique
Environmental impact: Dirty mining of precious metals can impact the environment. Mining companies generate about 20 tons of toxic waste for every 0.333-ounce gold ring.
Titanium
This versatile 3D printing material is a low-density, high-strength metal with a very high melting point.
You can use titanium for:
- Tooling
- Functional models
- Manufacturing
Pros:
- High-resolution
- Heat-resistant
- Highly durable
Cons:
- Very expensive
- Can easily explode in powder form, requires special atmosphere
Environmental impact: Titanium is one of the most eco-friendly materials:
- It doesn’t deteriorate, making it easier to recycle
- Its low weight reduces energy required to transport it
Ceramic
A ceramic is an inorganic solid made up of compounds that have been shaped and hardened by heating to high temperatures.
You can use ceramic for:
- Visual arts
- Manufacturing
Pros:
- Heat-resistant
- Hard-wearing
- Affordable
Cons:
- Fragile
- Has fewer applications
Environmental impact: Ceramics require a great deal of heat to produce, but there are ways to practice sustainability when working with ceramics:
- Collect glaze waste for reuse in future ceramic projects
- Collect ceramic waste, then crush for use in general construction
Learn more about 3D printers, including HP®'s industrial metal printer and how 3D printers work on HP® Tech Takes.
Infographic sources:
- All3DP; 3D Printing Materials Guide
- 3DEO; Pros and Cons of 3D Printing Metal Components
- i.materialize; 8 Interesting Facts about 3D Printing
- 3D Printing; 3D Printing Materials
- Tinkercad; 3D Printing Materials Guide
- Simplify 3D; Ultimate 3D Printing Material Guide
- Engineering.com; 9 Desktop 3D printing Resins You Should Know About
- 3DPrint.com; How, When, Why: A Guide to 3D Printing with Titanium
- Grist; What's the most eco-friendly material for a 3D printer?
- Good on You; Material Guide, How Sustainable is Nylon
- Titanium is Nifty; Environmental Impact
- Brilliant Earth; Gold Mining and the Environment
- SASSDA; Stainless Steel and the Environment
- Appropedia; Polymer Environmental-friendly Resin
- Science Daily; Chemists develop fully biodegradable and recyclable synthetic resin
- Ceramic Arts Network; Sustainability in the Ceramic Studio
Article reposted with permission from HP Tech Takes






